How Do the Secondary Structures of Dna and Rna Differ
Non-crossing If b i b. The basepairing of complementary nucleotides gives the secondary structure of a nucleic acid.

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Or the ordered arrangement of nucleic acid.

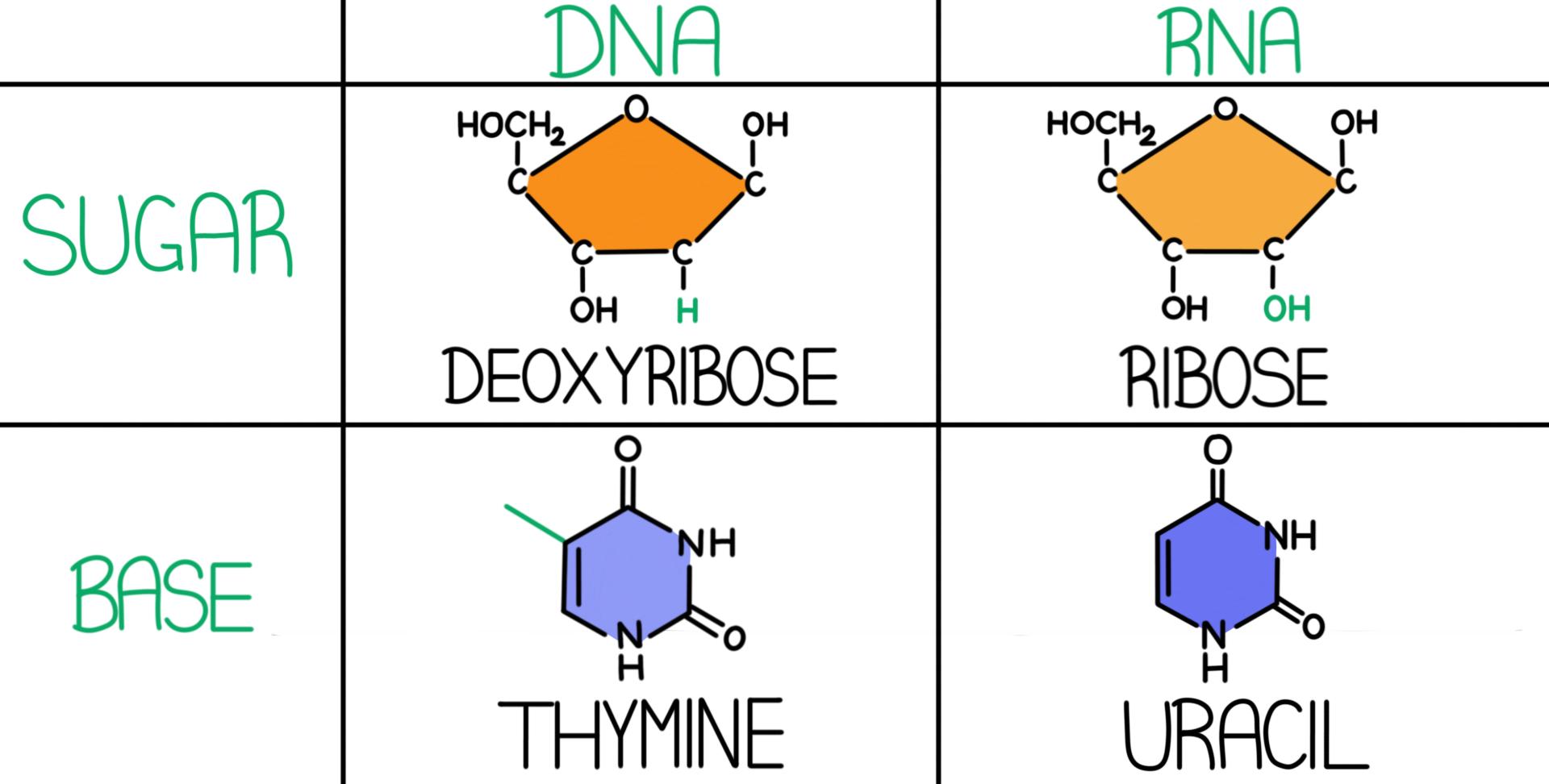
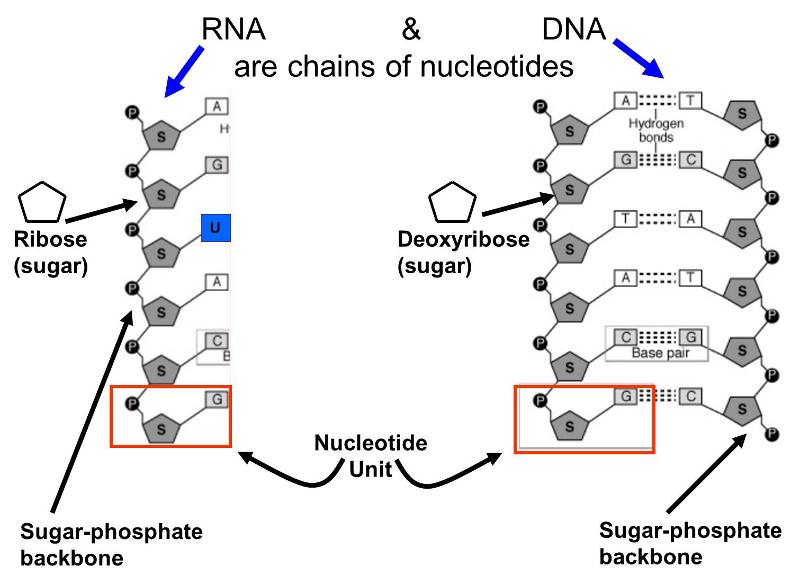
. DNAs second structure consists of two antiparallel strands twisted into a double helix. The existence of a molecule in a keto lactam and enol lactim form is known as tautomerism. DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA.
RNA Secondary Structure Secondary structure. This entry was posted on August 23 2020 by Anne Helmenstine updated on March 21 2022 Three differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA uses the base thymine while RNA uses uracil DNA uses the sugar deoxyribose while RNA uses ribose and usually DNA is double-stranded and RNA is single-stranded. D Only RNA and not DNA has a primary structure.
If b i b j S then i j - 4. In a doublestranded DNA or RNA this refers to the WatsonCrick pairing of complementary strands. This was considered to be the greatest discovery of modern biology and hence they got Nobel prize for the same.
DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA. For example the cloverleaf. The secondary structure of DNA was proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953.
They proposed that DNA is a double helix containing two polynucleotide strands wound as if around a central axis. On the contrary after heating the DNA molecules behaved like. This three-dimensional arrangement is called the tertiary structure of RNA and it can be very.
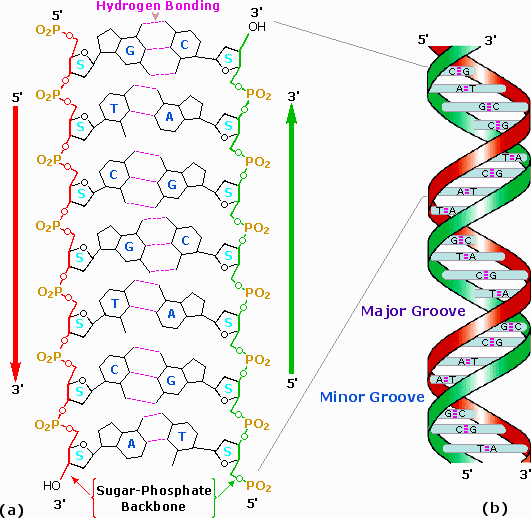
In a singlestranded RNA or DNA the intramolecular base pairs between complementary base pairs determines the secondary structure of the molecule. The fundamental characteristic of DNAs secondary structure is that it consists of two polynucleotide strands wound around each other known as the double helix. The RNA tertiary structure is the result of RNA folding which creates a three-dimensional shape consisting of helices and grooves.
RNA bases form hydrogen bonds with complementary bases on the same strand forming hairpin loopsDNA forms hydrogen bonds with complimentary bases on a different strand. Sponk Creative Commons 30 DNA. RNA molecules are variable in length but much shorter than long DNA polymers.
What type of bonds connect the nitrogenous bases of the complementary DNA strands. These two processes are descibed in the theory of compensatory substitutions section. What is the base pairing rule in DNA structure.
Generally mRNA secondary structures like hairpin loop stem will cause interference with the translation of protein. Explain what it means when we say the two strands of the DNA helix are antiparallel. RNA sometimes forms a secondary double helix structure but only intermittently.
The base pairing via hydrogen bonds is the basis of RNA secondary structure. The secondary structures of biological DNAs and RNAs tend to be different. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose but RNA has ribose in the same position.
RNA only has one strand but like DNA is made up of nucleotides. What is the difference in their primary structure. As is observed in the Fig.
The secondary structure of DNA consists of mainly B-form double helix while the secondary structure of RNA consists of short regions of A-form of a double helix. B Adenine pairs with thymine in DNA while adenine pairs with uracil in RNA. The main function of RNA is to carry information of amino acid sequence from the genes to where proteins are assembled on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
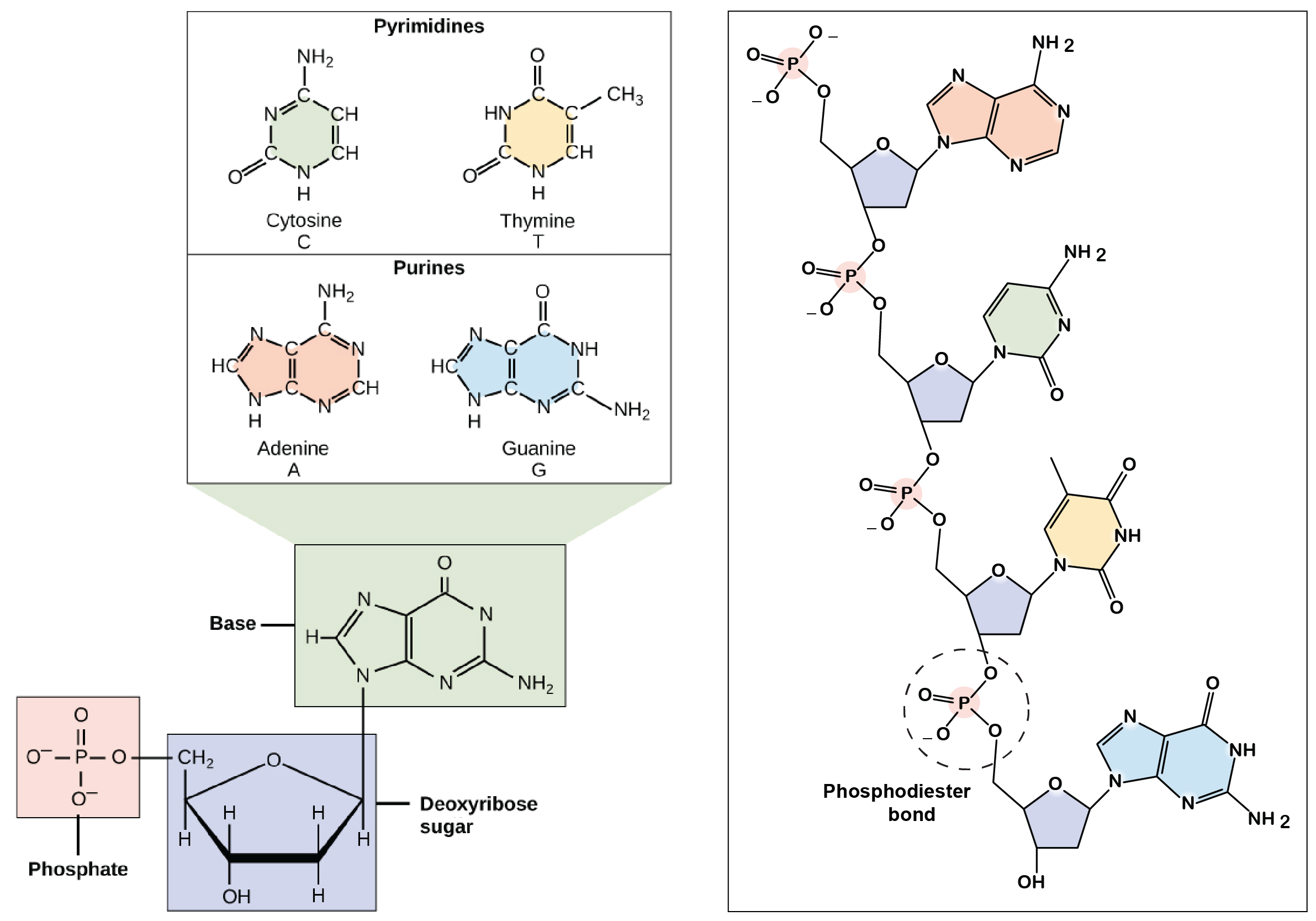
The sugar-phosphate linkages are on the outside of the helix and the bases are stacked in the interior of the molecule as shown in the figure. A DNA contains the sugar ribose while RNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. It can be represented as a list of bases which are paired in a nucleic acid molecule.
Watson-Crick S is a matching and each pair in S is a Watson-Crick pair. A set of pairs S b i b j that satisfy. RNA differs from DNA in that it contains a uracil nucleotide instead of thymine and carries a 2 hydroxyl group rather than a 2.
How do DNA and RNA differ. Nucleic acid secondary structure is the basepairing interactions within a single nucleic acid polymer or between two polymers. C Guanine pairs with cytosine in DNA while guanine pairs with adenine in RNA.
Non Watson-Crick base pairing where guanine pairs with uracil is allowed in RNA but not in DNA. Complementary base pairing between purine and pyrimidine bases. The difference in the sugars gives rise to differences in their secondary and tertiary structures.
How do the structures of RNA and DNA differ. DNA contains thymine T whereas RNA contains uracil U. The base- pairing that occurs in RNA is all through regions of self-complementarity.
Biological DNA mostly exists as fully base paired double helices while biological RNA. Difference between DNA and RNA. Common Secondary Structures of RNA The main difference between the three-dimensional structures of DNA and RNA is that in RNA the three-dimensional structure is single-stranded.
-primary structure of nucleic acids is the order of bases in the polynucleotide sequence. Some observations made on deoxyribonucleic acids in solution suggested that DNA molecules as they could be extracted from cells had structural characteristics different from those expected in molecules having only the primary structure we just described. Two significant differences between DNA and RNA 1 Sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is deoxyribose and of RNA is ribose 2 DNA contains the.
Given a DNA or RNA sequence the. A-U U-A C-G or G-C. The process can be a single step process double substitution or a two step process two single substitutions.
RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands. -secondary structure is the 3-dimensional conformation of the backbone. Secondary Structure of Deoxyribonucleic Acids.
Describe the secondary structure of DNA. The secondary structure is left unchanged when complementary substitutions occur in the DNA gene coding for the RNA molecule. 22 thymine and uracil differ in structure by the presence in T or absence in U of a methyl group.
No sharp turns The ends of each pair are separated by at least 4 intervening bases.
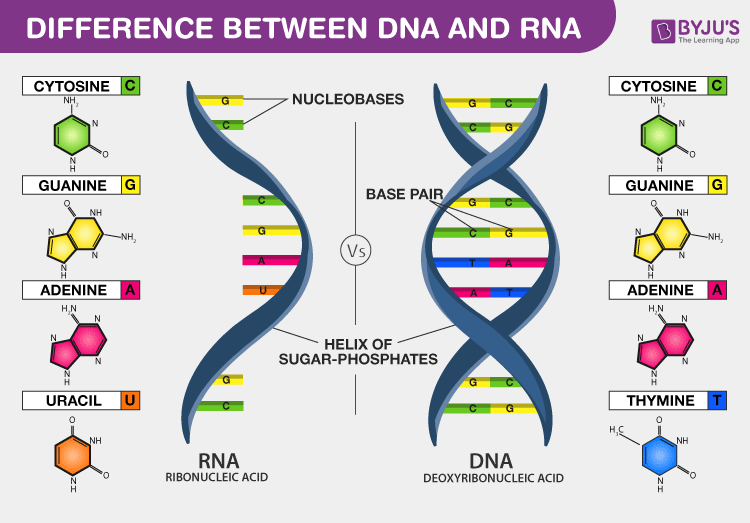
Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna

Do You Know The Differences Between Dna And Rna Biology Notes Study Biology Teaching Biology
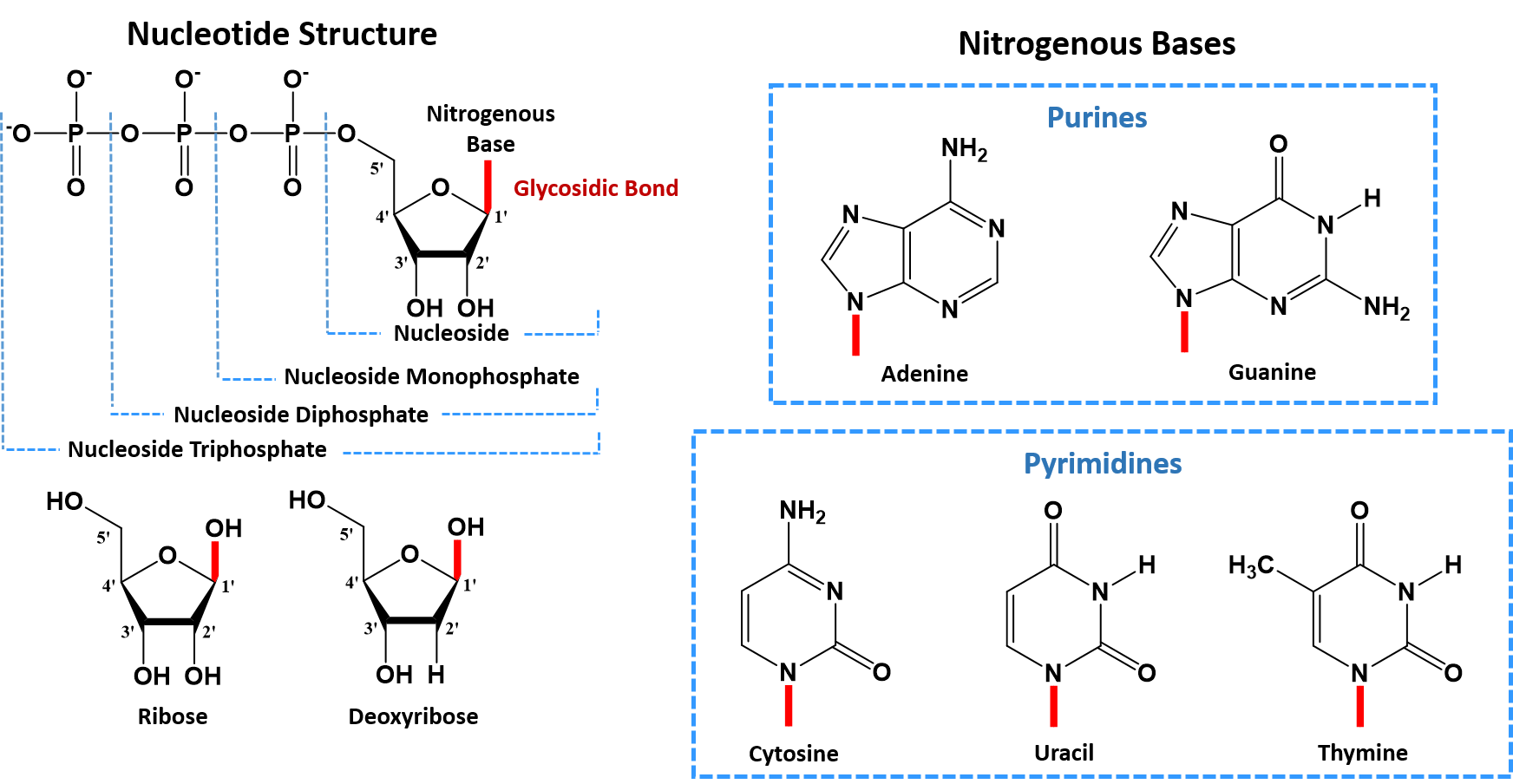
Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry
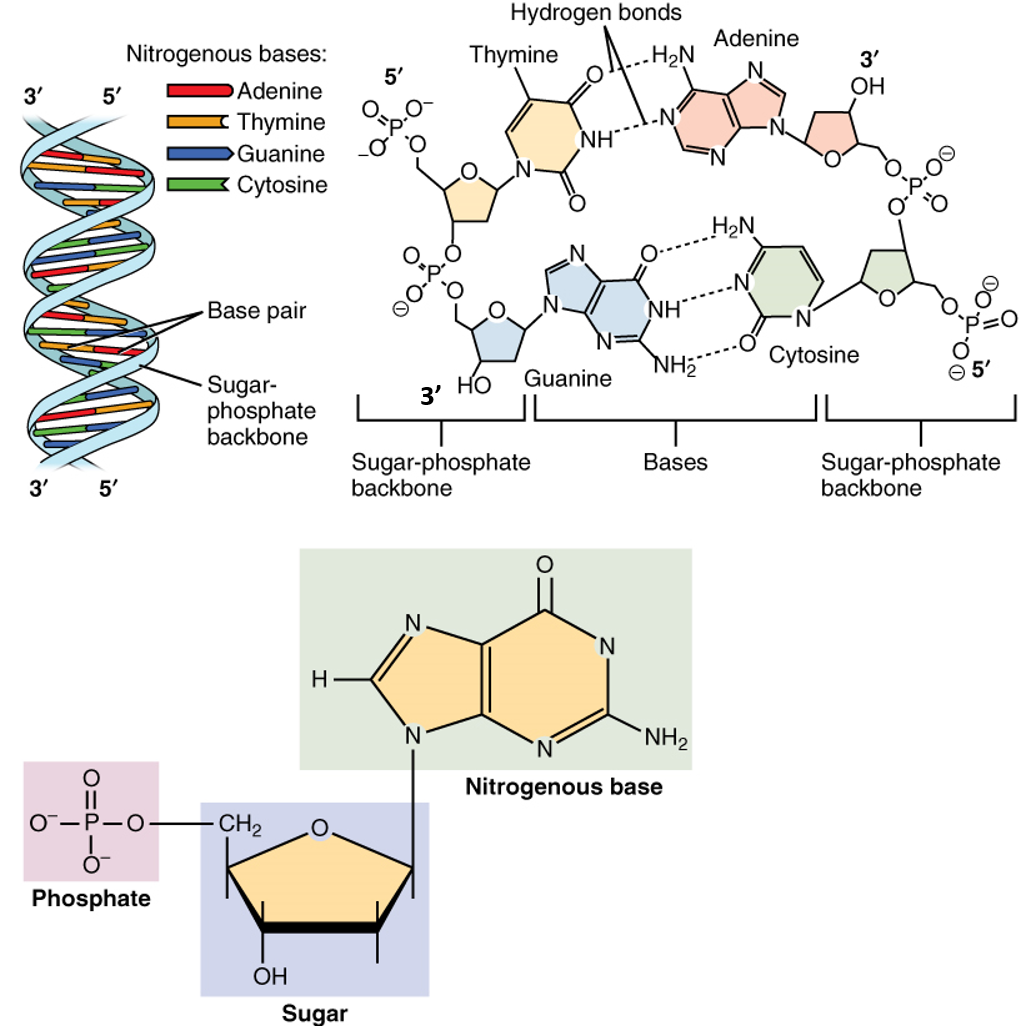
Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Di Erences And Comparison

Origins Of Cell Compartmentalization Ap Biology Biology Dictionary
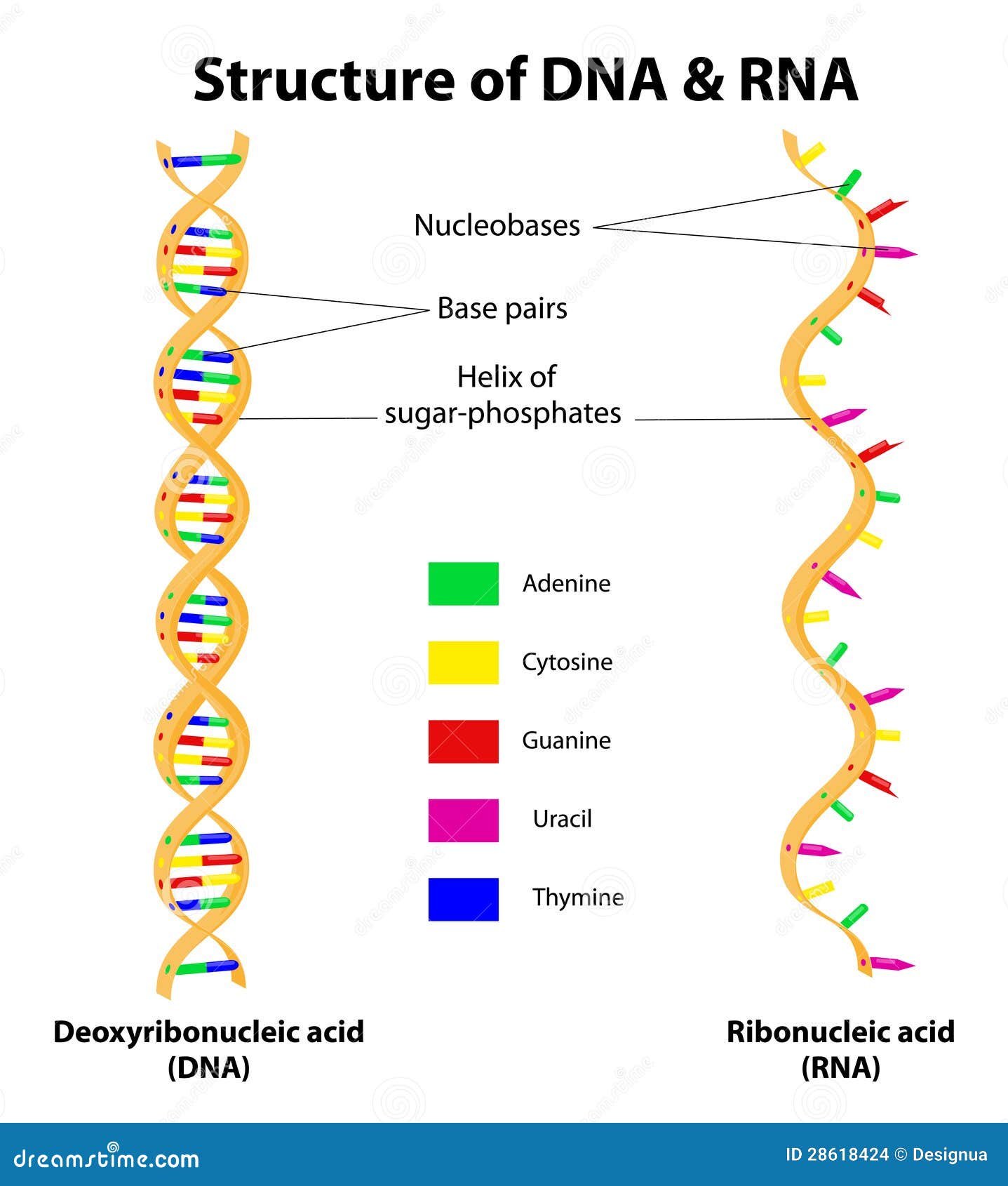
Rna Stock Illustrations 8 054 Rna Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy
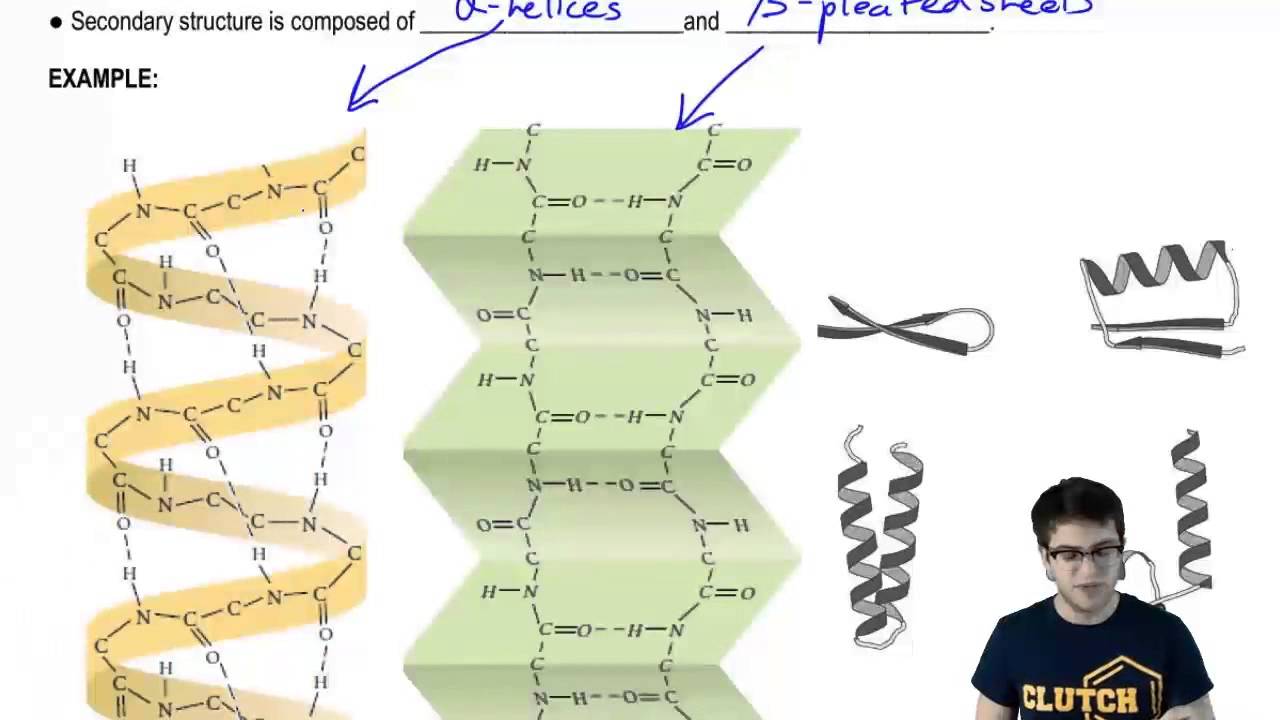
Primary And Secondary Structure Youtube

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Dna Vs Rna Vector Illustration Vectormine Biology Lessons Biology Classroom Teaching Biology

Nucleic Acid Types And Structure Biology Dictionary
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Comments
Post a Comment